Introduction

With the rapid development of science and technology, LED display screens, as an important carrier of modern information display, have been widely used in various fields. To understand and apply LED display screens deeply, it is particularly important to master their working principles.
The working principle of LED display screens involves knowledge in many fields, such as electronics, optics, material science, etc. It is a complex and exquisite system.
By in-depth understanding of the basic concepts of LED, the composition of the display screen, and the driving and control mechanisms, we can better grasp the performance characteristics of the LED display screen, thereby maximizing its value in practical applications.
1. How is an LED display different from other display technologies?
Compared with other display technologies, LED displays do have obvious differences. LED display screen attracts people’s attention with its unique light and charm. Although other display technologies have their characteristics, they often appear slightly inferior in the sharp contrast of LED displays.
- From the working principle:
The LED display screen is more like a precise conductor. By accurately controlling the current, each LED lamp bead can achieve its best effect.
The LCD display is more like a meticulous painter, outlining the image stroke by stroke through the arrangement of liquid crystal molecules.
The OLED display is like a free dancer, and its self-illuminating characteristics enable it to show a smoother and more natural picture.
- In terms of display effect:
The LED display screen has bright colors and high contrast, just like a colorful oil painting, showing every detail vividly. Although the LCD display also produces a clear picture, the colors and contrast may be a little flat in comparison.
The OLED display shows a deep and three-dimensional picture effect with its high contrast and wide viewing angle.
- In terms of energy consumption and lifespan:
LED displays stand out in terms of their lower power consumption and longer lifespan.
This makes it the preferred solution for energy conservation and environmental protection, providing a reliable guarantee for long-term use. LCDs are also constantly improving in terms of luminous efficiency, while OLED displays also have their own unique features in terms of energy saving.
- From the perspective of structure and application:
An LED display screen is like a changeable puzzle that can be spliced into various shapes and sizes as needed. Whether it’s a large outdoor billboard or a display in a sports venue, it can handle it with ease.
The LCD is more like a fixed picture frame, which can only display the picture within a limited range. As for the OLED display, it is like a freely bendable canvas, providing unlimited possibilities for innovative applications such as wearable devices and curved TVs.
2. What are the basic components of an LED display?
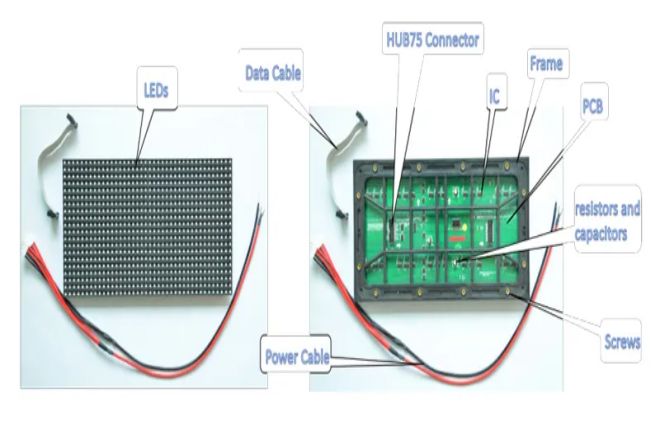
The basic components of an LED display screen mainly include the following parts:
The LED module is the basic unit of the LED display screen, usually composed of multiple LED lamp beads, a circuit board, a power supply, and a control chip. LED lamp beads are the most basic light-emitting unit of the display screen, and their quality directly determines the display effect of the display screen.
The control chip is responsible for controlling the brightness and color of the LED lamp beads to ensure that they emit light as required.
- Drive circuit:
The drive circuit is an important part of the LED display screen and is responsible for providing stable current and voltage to the LED lamp beads to ensure their normal operation. The drive circuit usually includes power management, brightness adjustment, grayscale control, scanning control, and other functions to achieve an accurate display of the picture.
- Auxiliary structures:
LED displays usually require some auxiliary structures to support and fix the LED modules, such as metal or aluminum alloy frames. In addition, there are radiators, dust covers, sunshades, etc., to provide protection and a stable working environment.
- Data lines and cables:
Data lines and cables are used to connect LED modules, control cards, power supplies, and other equipment to achieve data and power transmission. They ensure that information flows between the various parts so that the display can function properly.
- Housing and screen:
The housing is usually made of metal or plastic and is used to protect the internal equipment of the LED display and provide support and fixed installation. The screen is the part that users watch directly, and its quality directly affects the viewing experience.
In addition to the basic components mentioned above, software and firmware are also important parts of the LED display function. Although they are not physical components, they play a vital role in realizing the display function.
3. How does the power consumption of LED displays compare to other display technologies?
Compared with other display technologies, the power consumption performance of LED displays is generally excellent. The amount of power consumed depends on several factors, including the size of the display, pixel density, brightness, and the efficiency of the technology used.
Generally speaking, LED displays have higher light efficiency and lower power consumption. LED (Light Emitting Diode), as a solid-state light source, has the characteristics of high-efficiency conversion and long life. Compared with traditional CRT (cathode ray tube) displays, LED displays consume much less power. Compared with LCD (liquid crystal display), LED displays tend to have lower power consumption under the same brightness and color performance.
However, the specific performance of power consumption is also affected by the specific model, configuration, and usage conditions. Different brands and models of LED displays may have differences in power consumption. In addition, when using high brightness, high resolution, or special display modes, power consumption may increase accordingly.
In order to reduce the power consumption of LED displays, a variety of technologies and methods can be used. For example, optimizing the refresh frequency, using low-power display modes, and rationally designing display content and layout can reduce power consumption to a certain extent.
In addition, choosing high-efficiency LED lamp beads and drive circuits, as well as adopting reasonable heat dissipation design, can also help reduce power consumption and extend the life of the display.
It should be noted that power consumption is only one aspect of evaluating the quality of display technology. Other factors such as display effect, cost, and reliability also need to be comprehensively considered. Therefore, when choosing display technology, you need to make trade-offs and choices based on specific application scenarios and needs.
4. How are images and videos displayed on the LED display?

The image and video display process on the LED display is a complex and delicate technical process involving the collaborative work of multiple key links and components.
First, image and video data are transmitted to the LED display control system through data lines. This control system usually consists of a main control board or control card, which receives signals from a computer or other video sources and decodes and processes these signals.
Next, the processed image and video data are converted into instructions for controlling the LED lamp beads to emit light. These instructions are sent to each LED module through the driver circuit.
The drive circuit is an important part of the LED display screen. It is responsible for converting the control signal into appropriate current and voltage to drive the LED lamp beads to emit light.
After receiving instructions from the driving circuit, each LED lamp bead will emit light according to the instructions’ brightness and color requirements.
For color LED displays, each pixel is usually composed of three LED beads: red, green, and blue. By precisely controlling the brightness and color of these three lamp beads, rich colors can be mixed.
When tens of thousands of LED lamp beads emit light at the same time, they together form the images and videos on the LED display.
Because each pixel can be controlled independently, the details and colors of the image can be accurately displayed to achieve high-definition, lifelike visual effects.
In addition, in order to improve the display effect and reduce energy consumption, LED displays also use a variety of technologies.
For example, grayscale control technology can adjust the brightness level of LED lamp beads to achieve a smoother brightness transition; scanning control technology can optimize the scanning method of LED lamp beads and improve display speed and stability.
5. What are the advantages of LED displays over traditional display technologies such as LCD or plasma?
LED displays have a series of significant advantages over traditional display technologies such as LCD or plasma.
First of all, from a power consumption perspective, LED displays generally have lower power consumption. As a solid-state light source, LED (light-emitting diode) has the characteristics of high-efficiency conversion and can consume less power at the same brightness.
In comparison, LCD (liquid crystal display) and plasma displays can be higher in terms of power consumption. Therefore, LED displays can significantly save energy costs in long-term operation and large-scale applications.
Secondly, LED displays have advantages in brightness and contrast. LED displays can provide higher brightness and sharper contrast, making images and videos clearer and more vivid.
Whether in indoor or outdoor environments, LED displays can maintain excellent visual effects without being disturbed by light.
In addition, LED displays have a longer life and higher reliability. LED lamp beads generally have a long life and can withstand long-term use and high-intensity working conditions.
At the same time, the structural design of the LED display is also more sturdy and durable and can adapt to various complex environments and installation conditions.
In terms of color performance, LED displays also perform well. It can present a wider color range and more accurate color reproduction, bringing users a more realistic and vivid visual experience.
Whether used for advertising displays, commercial promotions, or other application scenarios, LED displays can meet users’ needs for high-quality images and videos.
Finally, LED displays also have advantages in terms of environmental protection.
Due to its low power consumption and long life, LED display screens can reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions during use, which is in line with the green environmental protection concept of modern society.
Conclusion
In summary, an in-depth understanding and application of the working principles of LED displays are the key to promoting its technological progress and market development. In the future, with the continuous innovation of science and technology and the continuous expansion of application fields, LED displays will play an important role in more fields.
Finally, if you want to know more about LED displays, please get in touch with us.
