소개

Have you noticed that whether it’s a large advertising screen in a 쇼핑몰 or a dazzling LED screen on a stage.
They all stay lit for long periods every day, yet why are some screens inexpensive in terms of electricity, while others are shockingly expensive?
Actually, there’s a big secret behind this—the energy efficiency design and energy-saving technology of LED displays.
목차
1. How Does an LED Display Work?

An LED display is actually composed of thousands of tiny LED beads. Each bead typically contains red, green, and blue LEDs, which mix to create various colors by adjusting their 명도.
The basic building block of the screen is the LED module. Like building blocks, many modules are combined to form a complete large screen.
When the screen receives an image or video signal, the control system tells each LED bead how bright it should be and what color it should display.
The red, green, and blue LEDs quickly turn on and off, mixing colors to form a complete image in our eyes.
Because LEDs are self-emissive, each LED bead can independently control its brightness.
Therefore, the screen can achieve high brightness, high contrast, and dynamic images without ghosting, even remaining clearly visible in sunlight.
Compared to traditional LCD screens, LED screens are more energy-efficient and durable.
LCDs require backlighting, keeping the entire screen lit, even when displaying black, consuming power.
LEDs, on the other hand, only illuminate the areas that need to be displayed, resulting in significantly higher energy efficiency.
Furthermore, LEDs offer more vibrant colors, deeper blacks, brighter whites, and a longer lifespan, easily reaching tens of thousands of hours.
Another advantage of LED screens is their modular design: if a section of the screen fails, only that module needs to be replaced, allowing the entire screen to continue operating and simplifying maintenance.
2. Why are LED displays more energy-efficient?

LED displays are energy-efficient primarily due to their low power consumption and flexible control. Each LED can be individually switched on and off.
Illuminating only the areas that need to be displayed, a significant difference from traditional LCD screens.
For example, if most of the screen is black or a dark area, the LEDs can be completely turned off.
While an LCD screen, even when displaying black, requires the entire backlight to be on, wasting considerable energy.
Besides the ability to switch on and off as needed, LEDs also have high photoelectric conversion efficiency.
In other words, with the same power, LED screens can display brighter images than LCD or OLED screens, which is why LEDs are so popular in outdoor large screens or 단계 displays.
While OLEDs can also emit light from each pixel, large-sized screens are expensive, energy consumption is not low during prolonged high-brightness use, and their lifespan is shorter than LEDs.
Therefore, for long-term use and large-area displays, LEDs are more energy-efficient and durable.
The benefits of energy saving are not only reduced electricity bills but also significantly lower operating costs.
을 위한 쇼핑몰 advertising screens, outdoor billboards, conference room large screens, or concert stage screens, the electricity costs for long-term operation are considerable.
The low energy consumption of LED screens means reduced electricity expenses, and the modular design makes maintenance easier.
If a screen module fails, only that module needs to be replaced, without affecting the entire screen’s operation.
Overall, the operating cost is much lower than traditional displays.
3. How do brightness and contrast affect the energy efficiency of LED displays?

그만큼 명도 and contrast of LED displays not only affect how clear the image appears but also directly determine power consumption.
The higher the screen brightness, the more power it consumes; conversely, too low brightness makes the image difficult to see in bright light, so finding the right brightness is crucial.
Modern LED screens typically have brightness adjustment functions that automatically adjust brightness based on ambient light.
For example, in bright daylight, the screen automatically brightens to ensure clear visibility.
At night or in dim light, the screen brightness decreases, protecting eyes and saving power.
This intelligent adjustment allows the screen to maintain a good image in different environments while avoiding wasted electricity.
Contrast ratio also affects energy consumption. High contrast means deeper blacks and brighter whites.
When displaying black content, the LEDs can be partially or completely turned off, saving much more power than keeping the entire screen on.
For example, when displaying text, charts, or content against a dark background, high contrast illuminates only the necessary areas, with black areas consuming almost no power.
To find a balance between brightness and energy saving, several methods can be used:
자동 밝기 조정: Allow the screen to automatically adjust based on ambient light intensity.
Local brightness control: Illuminate only the areas that need to be displayed, turning off or reducing the brightness of black areas.
Properly set contrast: Ensure a clear image without wasting electricity.
Using these methods, LED displays can be clearly seen in sunlight while saving electricity, achieving a balance between visual appeal and energy efficiency.
4. What is the energy efficiency difference between direct backlighting and edge backlighting?
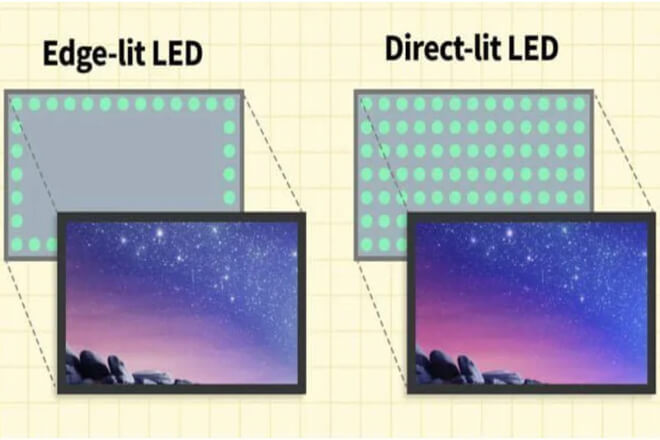
The backlighting method of an LED display directly affects energy efficiency and image quality.
There are two common methods: direct backlighting (Direct LED) and edge backlighting (Edge LED).
Direct backlighting places the LED chips directly behind the screen, with each area of the screen supported by LEDs.
Because the light source is evenly distributed, the image brightness is more uniform, and the contrast is better.
At the same time, due to direct light illumination, there is less light energy loss, resulting in relatively higher energy efficiency.
Especially in large screens or outdoor screens requiring high brightness, direct backlighting can minimize power waste while ensuring clarity.
Edge backlighting, on the other hand, places the LED chips at the edge of the screen and uses a light guide plate to evenly distribute the light across the entire screen.
While this method is cheaper to manufacture and allows for thinner screens, it introduces some light loss as light must pass through a light guide plate.
To ensure brightness, the power of the LED chips needs to be increased.
Therefore, in large-size or high-brightness scenarios, edge-lit backlighting typically consumes more energy than direct backlighting.
In practical applications, if high brightness, high uniformity, and lower energy consumption are desired, direct backlighting is the ideal choice.
For thin, light, low-power displays intended for close-range viewing, edge-lit backlighting can meet the requirements.
But its energy efficiency is not as good as direct backlighting in large screens or outdoor environments.
Simply put, direct backlighting is like each pixel having its own “little light bulb,” providing uniform and energy-saving illumination。
Edge-lit backlighting is like illuminating the entire screen from the edge, requiring light to travel to achieve uniformity, resulting in slightly higher energy consumption.
Choosing the appropriate backlighting method based on the application scenario allows for finding the optimal balance between brightness and energy efficiency.
| Feature | Direct Backlight (Direct LED) | Edge Backlight (Edge LED) |
|---|---|---|
| Light Source Position | LEDs are placed directly behind the screen | LEDs are placed at the edges and light is guided across the screen |
| Brightness Uniformity | High, light is evenly distributed across the screen | Medium, depends on light guide panel for even distribution |
| Contrast Performance | Good, deep blacks and bright whites | Average, bright areas may have slight light leakage |
| Energy Efficiency | High, minimal light loss | Lower, needs higher power to compensate for light loss |
| Typical Applications | Large screens, outdoor advertising, stage displays | Small screens, thin displays, close-up viewing |
| Screen Thickness | Thicker | Thinner |
| Manufacturing Cost | 더 높은 | Lower |
5. How does intelligent adjustment help improve the energy efficiency of LED displays?

Intelligent adjustment is like giving the LED display a “brain,” allowing it to “use electricity smartly.”
The most common technology is automatic brightness adjustment: the screen automatically adjusts its brightness based on the ambient light intensity.
For example, in strong sunlight during the day, the screen automatically brightens to ensure that advertisements, videos, or information are clearly displayed.
At night or in low light, the screen automatically dims, which is not only less glaring but also saves a significant amount of electricity.
In addition, many modern LED displays are equipped with environmental sensing systems, essentially giving the screen “eyes.”
The system can monitor changes in ambient light in real time and automatically adjust brightness and contrast accordingly.
For example, in cloudy or dimly lit indoor environments, the screen 명도 will decrease to reduce energy consumption.
When exposed to strong sunlight, the screen will quickly increase its brightness to ensure the image remains clearly visible.
Through this intelligent adjustment, LED displays can not only present clear images in various environments but also significantly reduce energy consumption, extend screen life, and reduce operating costs.
Simply put, intelligent adjustment allows the screen to “turn on the lights as needed,” presenting the best effect with minimal power consumption, keeping the image bright and energy-efficient.
6. How are the long-term energy-saving effects of LED displays manifested?

The energy-saving advantages of LED displays are not only apparent in terms of instantaneous power consumption, but become more evident over long-term use.
LED chips themselves are highly efficient and have a long lifespan. Combined with brightness adjustment and intelligent sensing technology, the screen consistently uses electricity “smartly” during daily operation.
을 위한 쇼핑몰 advertising screens, 옥외 광고판, or large stage screens, these screens operate for extended periods every day, resulting in significant cumulative electricity savings.
Even better, these energy-saving technologies extend the screen’s lifespan. Brightness and contrast automatically adjust according to the environment.
Preventing the chips from burning out or overheating due to prolonged full-brightness operation.
This makes the screen less prone to aging, reduces malfunctions, and simplifies replacement, making maintenance much easier.
Simply put, the long-term energy-saving effect of LED displays is like “the more you use it, the more energy-efficient it becomes”: not only does it save electricity daily.
But it also reduces maintenance and operating costs in the long run, making the screen last longer and be more reliable.
In other words, buying an LED screen is not just about immediate energy savings, but also about long-term cost savings and peace of mind.
7. What are the standards and certifications for LED display energy efficiency?

When choosing an energy-efficient LED display, it’s essential to consider not only specifications but also whether it meets energy efficiency standards and certifications.
These standards and certifications act like an “energy-saving ID card” for the screen, indicating that the device meets standards in terms of power consumption and environmental friendliness.
Common standards include:
Energy Star: A US energy efficiency certification indicating that the product meets strict power consumption standards and saves electricity over long-term use.
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): While primarily an environmental requirement, RoHS-compliant LED screens typically use safer and more environmentally friendly materials, indirectly contributing to reduced energy waste.
CE, UL, and other safety and energy efficiency labels: While these certifications lean towards safety, some products also meet certain energy efficiency standards.
These certifications provide consumers with a reference point when purchasing LED displays.
For example, for screens of the same size and brightness, one with Energy Star certification and one without will be more energy-efficient and reliable in the long run.
In other words, certification not only helps you choose energy-efficient products but also reduces long-term operating costs, preventing you from buying power-hungry and prone-to-problem equipment.
Simply put, energy efficiency certification is your “protective shield” when buying LED screens, helping you choose products that are both energy-saving and reliable.
8. 결론
Overall, the energy-saving advantages of LED displays are not only reflected in low instantaneous power consumption but also in continuous energy savings over long-term use.
From automatic brightness adjustment, ambient light sensing, and backlighting methods to compliance with international standards and certifications, every technology is designed to make the screen smarter and more efficient.
Understanding these aspects allows you to not only choose a screen with sufficient brightness, a clear picture, and low power consumption but also to reduce operating costs and extend equipment lifespan.
Finally, if you would like to learn more about LED displays, 우리에게 연락해주세요.
