Introduction

When we buy Afficheurs LED, we often hear words like “this LED display has good heat dissipation.” Why do you say that? Is heat dissipation very important for LED displays? This article tells you the answer.
Table des matières
1. A brief introduction to the heat dissipation mechanism of LED displays
LED displays generate heat during operation. If the heat cannot be dissipated in time, the temperature of the LED chip will rise, which will affect its luminous efficiency and life.
Therefore, the heat dissipation mechanism is a very important part of the design of LED displays.
The heat of LED displays mainly comes from LED chips, drive circuits, and power modules.
1.1). LED chip heat generation:
When LED chips emit light, not all electrical energy can be converted into light energy, and a large part of it will be converted into heat energy.
Generally speaking, the electro-optical conversion efficiency of LED chips is about 30% – 40%. That is, 60% – 70% of the input electrical energy is converted into heat.
Moreover, the higher the temperature of the chip, the lower its luminous efficiency.
For example, an LED chip works well at normal temperature, but when its temperature rises due to poor heat dissipation, the light it emits will become dimmer, and the color may become inaccurate.
It’s like a light bulb, which will become dimmer or even burn out if it is too hot.
1.2). Heat generation of the drive circuit and power module:
In addition to the LED chip, the drive circuit and power module will also generate heat. The drive circuit is like the “commander” of the LED chip.
It controls the working state of the chip, and in this process, it consumes some electricity and generates heat. The power module, on the other hand, has to convert the input electrical energy into electrical energy suitable for the LED chip.
This conversion process is not 100% efficient, and some of the electrical energy will be converted into heat and dissipated.
If all this heat is trapped inside, the entire LED display will be like a “small stove,” getting hotter and hotter.
2. Chain reactions that may be caused by insufficient heat dissipation of the LED display

If the LED display has poor heat dissipation, there will be many problems, just like dominoes, one falls, followed by a series of troubles. Let’s talk in detail about the chain reactions caused by insufficient heat dissipation.
1). The performance of LED chips is greatly reduced
1.1). Luminosité becomes dim:
LED chips are very sensitive to temperature. Think about it: the chip works well at normal temperature, and the brightness is sufficient.
But if the heat dissipation is not good and the temperature rises, the brightness will become lower and lower.
Par exemple, un écran d'affichage LED extérieur will become gray and dim when the sun shines in the summer, and the heat dissipation cannot keep up.
The original bright picture becomes dim, and the content displayed cannot be seen clearly from a distance.
Data shows that for every 10°C increase in temperature, the luminous efficiency of the LED chip may decrease by 5%-10%. Once the brightness decreases, the effect of the entire display screen will be greatly reduced.
1.2). Color becomes messy:
The high temperature will also make the color of the LED chip deviate. It’s like painting. The color was adjusted well, but when the temperature rose, the pigment changed color.
Red may become orange, blue may become purple, and the color of the entire display screen will be messed up.
In some occasions where color requirements are particularly high, such as LED displays used in organiser performances and art des expositions, if the color is not accurate, the effect will be completely ruined.
1.3). Lifespan is greatly shortened:
LED chips are like people. Their “bodies” will age faster in high-temperature environments. The higher the temperature, the faster the components inside the chip age and the shorter the lifespan.
An LED chip that can be used for 50,000 hours may break down after 20,000 hours if it works at high temperatures for a long time.
This is like a car that can run 200,000 kilometers, but if it often runs in bad road conditions and high temperatures, it may be scrapped after 100,000 kilometers.
2). The drive circuit is in a bad mood
2.1). Components break down at any time:
The resistors and capacitors in the drive circuit are like “little bombs” at high temperatures, and they may break down at any time. For example, electrolytic capacitors are particularly sensitive to temperature.
High temperatures will cause the electrolytes inside them to evaporate, reduce their capacity, and finally fail directly.
Once these components are broken, the drive circuit will not work properly, and the display will have various problems, such as flickering, screen distortion, etc.
2.2). Signal transmission is messed up:
The high temperature will also affect the stability of the drive circuit, making the signal transmission messy.
The image signal that should have been accurately transmitted may be distorted and delayed at high temperatures. Just like when we make a phone call, if the signal is not good, the sound will be intermittent and unclear.
If there is a problem with the signal transmission of the LED display, the picture will be stuck and deformed, seriously affecting the viewing experience.
2.3). Short circuit risk increases greatly:
High temperatures may also melt the solder joints on the circuit board, which is like the foundation of a house, which is loose, and it is easy to have problems. Once the solder joints melt, it may cause a short circuit in the circuit.
At the least, the display cannot work properly, and at the worst, it may cause safety accidents such as fire. Imagine if a large outdoor LED display caught fire due to a short circuit; the consequences would be disastrous.
3). Reduced efficiency of the power module
3.1). Energy consumption is rising:
The power module is like a “lazy man” at high temperatures, and its working efficiency becomes particularly low.
It can efficiently convert the input power into the power required by the display, but when the temperature is high, it consumes more power to maintain the output power.
For example, a power module is 90% efficient at room temperature, but it may only be 85% at high temperatures.
In this way, the energy consumption of the display will increase greatly, which will not only waste electricity but also increase operating costs.
3.2). Frequent triggering of overheating protection:
The power module generally has an overheating protection function. When the temperature is too high, it will automatically shut down to prevent damage.
But if the heat dissipation is not good and the temperature cannot be lowered, the overheating protection will be frequently triggered.
This is like a person who is too tired to work and needs to take a break at any time. If the power module is frequently shut down, the display will frequently restart or fail to start, seriously affecting normal use.
4). The overall performance of the display screen deteriorates
4.1). Uniformity becomes a mess:
Poor heat dissipation will cause different temperatures in different areas of the display screen, which is like a piece of cloth; some places are darker, and some places are lighter.
The temperature of the LED chips in different areas is different, and the luminous effect will be different, resulting in uneven brightness and color differences.
In some occasions where high display effects are required, such as advertising screens in centres commerciaux and scoreboards in stades, poor uniformity will make the entire display screen look particularly ugly.
4.2). Reduced contrast:
The high temperature will also affect the contrast of the LED. Contrast is like the layering of the picture. The higher the contrast, the clearer and more three-dimensional the picture.
However, insufficient heat dissipation will reduce the contrast, and the picture will become blurred and dull, like an ink painting without layers.
Looking at such a display screen will make your eyes tired, and it will be difficult to see the details in the picture.
4.3). Longer response time:
The response time of the LED chip will be longer at high temperatures. The response time is like the reaction speed of a person. The shorter the response time, the smoother the picture.
However, poor heat dissipation will make the response time longer, resulting in ghosting and afterimages in dynamic pictures.
For example, when watching a football game, the players’ movements are very fast, but because the display screen has a long response time, there will be a smear on the screen, just like the players are running in slow motion, which seriously affects the viewing experience.
5). Increased safety hazards
5.1). Increased fire risk:
High temperature is an important factor in causing fire. Poor heat dissipation will cause the insulation material inside the display screen to age.
Once the insulation material fails, a short circuit may occur, generating electric sparks and causing a fire. Especially in some crowded places, such as shopping malls and theaters, once a fire occurs, the consequences are disastrous.
5.2). Increased risk of electric shock:
High temperatures may also melt the outer skin of the wire and expose the metal wire inside. Once the metal wire is exposed, people may get an electric shock if they accidentally touch it.
Electric shock will not only cause harm to people but may also cause other safety accidents.
5.3). Serious electromagnetic interference:
The performance of electronic components is unstable at high temperatures, which may cause electromagnetic interference. Electromagnetic interference is like an invisible “noise” that affects the normal operation of surrounding equipment.
For example, in an office, if the LED display screen has poor heat dissipation and generates electromagnetic interference, it may cause the computer next to it to crash and the printer to fail to work properly.
3. What are the methods for cooling LED display screens?
Don’t worry about the heat dissipation of LED display screens, you can easily solve it yourself! The following methods are simple and practical, and you can operate them without professional tools.
1). Basic heat dissipation method:
1.1). Let the LED display screen “breathe”
- Method:
Remove all the debris piled around the display screen (such as cardboard boxes, rag dolls, green plants, etc.), and don’t let them block the air outlet and air inlet.
You can imagine that the display screen is like a person who needs to breathe fresh air. If it is surrounded by things, it will “suffocate,” and the temperature will naturally rise.
- Suitable scenes:
Écran LED d'intérieur, advertising LED screen at the door of the shop.
- Effet:
It’s like opening a window for the display screen, the heat can be dissipated faster, the screen temperature can be reduced by 3-5°C, and it will not be so hot to the touch.
And with air circulation, the components inside the display screen can also “breathe” more smoothly and have a longer life.
1.2). Keep the LED display “away from the wall.”
Method:
Don’t stick the display tightly against the wall, leave a few centimeters of space. If it is hung on the wall, you can add a bracket to keep it away from the wall.
You can think of the display as a toaster. If it is close to the wall, the heat cannot be dissipated, and the bread (here refers to the display) will be burnt (overheated).
- Suitable scenes:
Office LED display, conference room LED display
- Effet:
The air behind can flow, the heat dissipation efficiency is improved, the display is not easy to overheat, and the life span is longer.
And staying away from the wall can also prevent the moisture on the wall from affecting the display.
1.3). Don’t let the air outlet “suffocate”
- Method:
Don’t put anything in front of the display to block the air outlet, such as green plants, decorations, etc. The air outlet is like the “mouth” of the display. If it is blocked, the heat cannot be discharged, and the display will be “uncomfortable”.
- Suitable scenes:
Shopping guide screens in shopping malls and ordering screens in restaurants.
- Effet:
The air outlet is unblocked, the hot air can be discharged in time, the display screen works more stably, and will not “freeze” easily. In addition, air circulation can reduce the accumulation of dust inside the display screen.
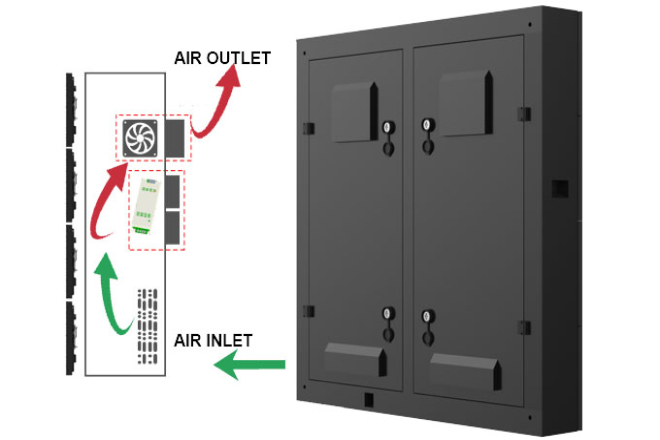
2). Low-cost transformation method:
2.1). “Install a small fan” for the LED display screen
- Method:
Install a small fan behind or on the side of the display screen (USB interface is fine, plug it into the computer and you can use it), and blow it towards the screen.
You can think of the fan as a “small air conditioner” to send cool breezes to the display screen. If there is not enough space behind the display screen, you can buy an ultra-thin fan, or fix the fan on the bracket.
- Suitable scenes:
Small LED display screens, home theater screens.
- Effet:
When the fan blows, the heat will dissipate, and the screen temperature can drop by 5-8°C, just like installing a small air conditioner for the display screen, which is cool.
And the sound of the fan is generally very small, which will not affect the viewing experience.
2.2). Install an air conditioner for the display
- Method:
Install an air conditioner that can cool inside the structure of the outdoor LED display
- Suitable scene:
Outdoor rear maintenance LED advertising screen
- Effet:
The temperature of the entire LED display can be reduced by 6-10°C, and it is not afraid of sun exposure in summer.
3). Daily maintenance method
3.1). Regularly “bathe” the display
- Method:
Use a soft brush or vacuum cleaner to clean the dust behind the LED display, especially the fan and heat dissipation holes, and don’t let the dust block them.
Dust is like a “small cotton jacket”, wrapping the display tightly, so that the heat cannot be dissipated. You can find time every month to clean the back of the display.
- Frequency:
Clean at least once a month. If there is too much dust, the heat dissipation will be poor.
- Effet:
With less dust, the heat dissipation will be smoother, and the display will have a longer life, and there is no need to replace it with a new one.
In addition, cleaning the dust can prevent the internal components of the display from being corroded.
3.2). Regularly check the “health” of the line
- Method:
Check whether the wires of the LED display are aging or damaged, especially the wires connecting the power supply and the fan.
If there is a problem, replace them quickly. The wires are like the “blood vessels” of the display screen.
If the blood vessels are blocked or broken, the display screen will “get sick.” You can check the circuit once a quarter to see if there are any black, hard, or broken areas.
- Frequency:
Vérifiez une fois par trimestre ; la sécurité est la plus importante.
- Effet:
En l'absence de problème avec le circuit, le système de refroidissement peut fonctionner normalement, évitant ainsi les risques de sécurité et permettant une utilisation en toute confiance. Une inspection régulière du circuit permet également de prévenir les accidents tels que les incendies.
3.3). Allumez et éteignez l'appareil de façon raisonnable ; ne le laissez pas « fatiguer ».
- Method:
Éteignez l'écran lorsque vous ne l'utilisez pas ; ne le laissez pas allumé en permanence, surtout pour dormir ou sortir. L'écran LED est comme une personne : il a besoin de repos. S'il est constamment allumé, il sera fatigué et sa durée de vie sera réduite.
- Suitable scene:
Écran d'affichage LED d'intérieur.
- Effet:
Réduisez la production de chaleur, prolongez la durée de vie de l'écran et économisez de l'électricité, faisant d'une pierre deux coups. Une consommation d'énergie raisonnable peut également réduire l'usure des composants internes de l'écran.
4. Quel est le principal défi de la conception de la dissipation thermique des écrans d’affichage LED ?
La conception de la dissipation thermique des écrans LED n'est pas simple. Elle nécessite de trouver un équilibre entre de nombreux aspects. Examinons en détail ces principaux défis.
1). Équilibre entre structure et dissipation thermique
1.1). La contradiction entre la tendance ultra-mince et l'espace de dissipation thermique
De nos jours, les écrans LED ultra-fins et légers sont très appréciés. Leur esthétique est certes esthétique, mais ils nuisent gravement à la dissipation thermique.
Pensez-y : plus l’écran est fin, moins il reste d’espace pour la dissipation de la chaleur.
C'est comme une petite pièce. À l'origine, on pouvait y installer un grand climatiseur pour rafraîchir la pièce, mais désormais, seul un petit ventilateur suffit.
L'effet de dissipation thermique peut-il être le même ? Les concepteurs doivent se creuser la tête pour concevoir une structure de dissipation thermique efficace dans un espace aussi restreint, par exemple en rendant le radiateur plus fin et plus dense ou en utilisant de nouveaux matériaux de dissipation thermique.
Que la chaleur puisse être dissipée à temps pour assurer le fonctionnement normal de l'écran.
1.2). Compromis entre étanchéité et dissipation thermique (conception étanche d'un écran extérieur)
Les écrans LED extérieurs doivent être étanches. Sinon, ils risquent de se briser en cas de pluie ; l'étanchéité est donc primordiale.
Mais si le joint est étanche, la chaleur ne peut pas sortir et l'efficacité de dissipation de la chaleur est considérablement réduite.
C'est comme mettre un imperméable sur un écran. Bien qu'il puisse empêcher la pluie, il est si chaud qu'il « transpire » sans pouvoir se dissiper.
Les concepteurs doivent trouver un équilibre entre l’étanchéité et la dissipation de la chaleur, par exemple en utilisant des matériaux et des structures d’étanchéité spéciaux.
Assurez l'étanchéité tout en permettant à la chaleur d'avoir un certain canal de dissipation thermique, ou concevez des canaux de dissipation thermique intelligents à l'intérieur de l'écran pour permettre à la chaleur de se dissiper le long de ces canaux.
2). Adaptabilité environnementale
2.1). Atténuation de l'efficacité de la dissipation thermique dans les environnements à haute température et à forte humidité.
Dans des environnements à haute température et à forte humidité, l'efficacité de dissipation thermique des écrans LED est considérablement réduite. La température élevée affaiblit le matériau de dissipation thermique et réduit l'efficacité du travail.
Une humidité élevée rend l'air vicié et la chaleur difficile à dissiper. C'est comme si une personne se trouvait dans un environnement étouffant et chaud et ressentait un malaise général, ce qui réduirait son efficacité au travail.
De plus, une humidité élevée peut également entraîner des problèmes de sécurité, tels que des courts-circuits à l'intérieur de l'écran d'affichage.
Par conséquent, les concepteurs doivent trouver des moyens de faire fonctionner normalement l’écran d’affichage dans un environnement à température et humidité élevées.
Par exemple, utilisez des matériaux de dissipation thermique résistants aux températures élevées et à l’humidité élevée ou concevez des structures de dissipation thermique spéciales pour dissiper la chaleur plus rapidement.
2.2). Contrainte thermique causée par des différences de température extrêmes
Les écrans d'affichage à LED peuvent être confrontés à des différences de température extrêmes pendant leur utilisation, par exemple lors du passage du froid extérieur au chaud intérieur.
Cette différence de température provoquera une contrainte thermique à l’intérieur de l’écran d’affichage, tout comme l’application d’une force invisible sur l’écran d’affichage.
Au fil du temps, les performances et la durée de vie de l'écran s'en trouvent affectées. C'est comme un morceau de verre, qui se brise facilement sous l'effet de la chaleur ou du froid.
Les concepteurs doivent réfléchir à la manière d’atténuer cette contrainte thermique, par exemple en utilisant des matériaux élastiques ou en concevant des structures capables d’absorber la contrainte thermique afin que l’écran d’affichage puisse rester stable sous des différences de température extrêmes.
3). Le jeu entre coût et performance
3.1). Pression sur les coûts des matériaux de dissipation thermique haut de gamme
Afin d'améliorer l'efficacité de la dissipation thermique, certains matériaux de dissipation thermique haut de gamme sont utilisés dans les écrans LED, tels que les nanofluides et les matériaux à changement de phase.
Ces matériaux sont certes faciles à utiliser et offrent une excellente dissipation thermique, mais leur prix est élevé. C'est comme acheter une voiture de luxe.
Les performances sont bonnes, mais le prix est prohibitif. Les concepteurs doivent trouver des solutions pour réduire les coûts tout en garantissant une bonne dissipation thermique.
Par exemple, voyez si certains matériaux rentables peuvent être utilisés pour remplacer ces matériaux haut de gamme ou, en optimisant la structure de dissipation thermique, réduire la quantité de matériaux utilisés, réduisant ainsi le coût global.
3.2). Consommation énergétique du système de dissipation thermique active
Les systèmes de dissipation thermique actifs, tels que les ventilateurs et le refroidissement par eau, peuvent en effet améliorer l'efficacité de la dissipation thermique, mais ils augmenteront également la consommation d'énergie de l'écran.
C'est comme si une personne courait pour faire de l'exercice, mais cela consommera également plus d'énergie.
Tout en recherchant des performances élevées, les concepteurs doivent trouver des moyens de réduire la consommation d’énergie et d’améliorer l’efficacité énergétique.
Par exemple, utilisez davantage de ventilateurs ou de pompes à eau économes en énergie ou concevez des systèmes de contrôle intelligents.
Ajustez la puissance de travail du système de refroidissement en fonction de la température de fonctionnement réelle de l'écran, afin que l'écran puisse trouver un équilibre optimal entre la dissipation thermique et la consommation d'énergie.
En bref, la conception de la dissipation thermique des écrans d’affichage LED est une tâche complexe et difficile.
Les concepteurs doivent trouver un équilibre entre de multiples aspects tels que la structure, l’environnement et le coût pour rendre l’écran d’affichage à la fois beau et pratique, efficace et économe en énergie.
5. Les avancées innovantes dans la technologie de dissipation thermique des écrans LED

Les avancées innovantes dans la technologie de dissipation thermique des écrans LED ont véritablement apporté des changements révolutionnaires à cette industrie.
Par le passé, nous avions toujours un casse-tête concernant le problème de dissipation thermique des écrans LED.
Aujourd'hui, avec l'émergence de nouvelles astuces telles que l'innovation des matériaux, l'optimisation structurelle et la gestion thermique intelligente, le problème de dissipation thermique n'est plus un problème et les écrans LED peuvent également fonctionner « froidement et rapidement ».
1). Innovation matérielle :
1.1). Graphène et nanotubes de carbone :
Le graphène et les nanotubes de carbone sont deux noms qui évoquent la haute technologie. Véritables « super-héros » de la dissipation thermique, ils offrent une conductivité thermique exceptionnelle.
Le graphène est un outsider parmi les matériaux de dissipation thermique. Il s'agit d'une couche mince, mais sa conductivité thermique est remarquable. Les nanotubes de carbone ne sont pas en reste, et leur conductivité thermique est également excellente.
Avec l'ajout de ces deux éléments, l'efficacité de dissipation thermique des écrans LED a considérablement augmenté et il n'y a plus lieu de s'inquiéter d'une « grève » de l'écran d'affichage en raison d'une surchauffe.
1.2). Nouveaux matériaux composites :
Outre le graphène et les nanotubes de carbone, de nouveaux matériaux composites brillent également dans le domaine de la dissipation thermique. Substrats céramiques et matériaux composites à base de métal : ces noms semblent assez « hardcore ».
Ils présentent non seulement une bonne conductivité thermique, mais également d’excellentes propriétés mécaniques et une stabilité chimique.
Tout comme le « joueur polyvalent » de la dissipation thermique, quel que soit le type d'environnement auquel ils sont confrontés, ils peuvent facilement y faire face et assurer le fonctionnement stable de l'écran LED.
2). Optimisation structurelle :
2.1). Technologie d'empilement 3D :
La technologie d'empilement 3D consiste simplement à « multiplier » l'espace de dissipation thermique. Auparavant, les écrans LED étaient ultra-fins et l'espace de dissipation thermique était limité, ce qui ne permettait pas d'améliorer l'efficacité de la dissipation thermique.
Désormais, grâce à la technologie d'empilement 3D, la puce LED et la structure de dissipation thermique peuvent être étroitement combinées, tout comme pour « créer » plus de zone de dissipation thermique dans un espace limité.
De cette façon, l’efficacité de la dissipation thermique augmentera naturellement et l’écran d’affichage LED pourra fonctionner de manière plus « froide ».
2.2). Conception bionique :
La conception bionique est une « inspiration naturelle » dans le domaine de la dissipation thermique. Les scientifiques se sont inspirés des créatures naturelles pour cette dissipation, par exemple en imitant la structure superficielle de la peau de requin.
Les fines lignes à la surface de la peau de requin optimisent l'écoulement de l'eau et réduisent la résistance. De même, l'application de cette conception à la dissipation thermique des écrans LED permet d'optimiser le flux d'air et d'améliorer l'efficacité de la dissipation thermique.
C'est comme mettre une « couche de dissipation thermique » sur l'écran d'affichage LED, lui permettant de dissiper la chaleur plus efficacement.
6. Conclusion
En général, la dissipation thermique n'est pas seulement liée à la stabilité des performances des écrans d'affichage LED, mais affecte également directement sa sécurité et sa durée de vie.
Bien comprendre l’importance de la dissipation thermique et choisir la bonne solution de dissipation thermique sont les questions fondamentales auxquelles chaque concepteur et opérateur d’écran d’affichage à LED doit prêter attention.
Enfin, si vous souhaitez en savoir plus sur les écrans d'affichage LED, Contactez nous s'il vous plait.
